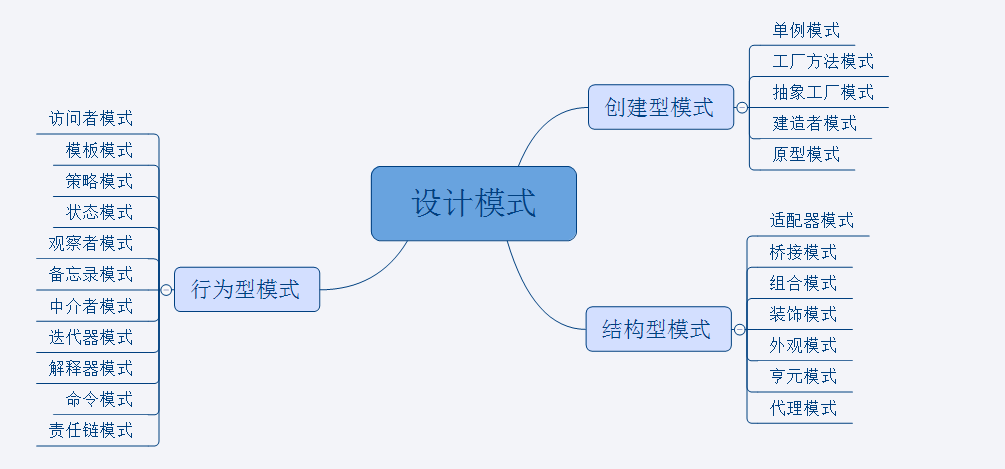
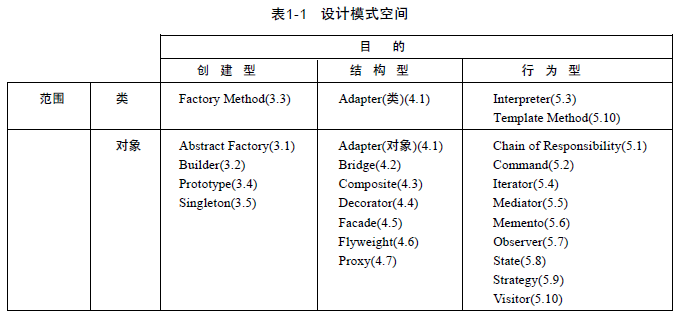
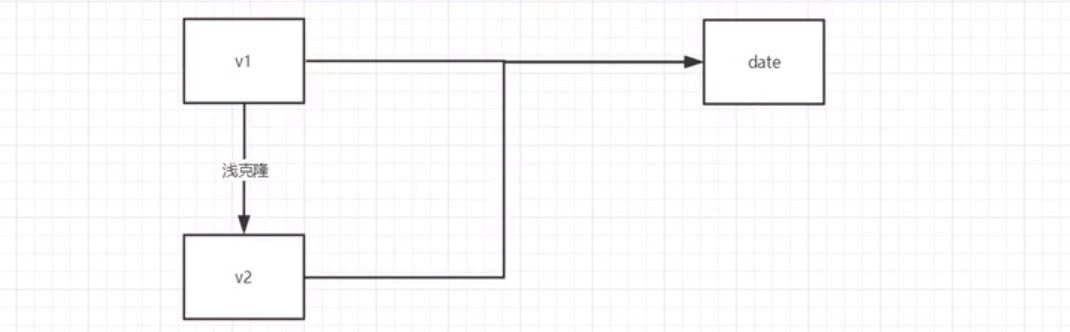
这一篇为第一篇介绍创建型模式,创建型模式一共有5种:
- 工厂模式
- 抽象工厂模式
- 单例模式
- 构造者模式
- 原型模式
一、工厂模式
定义:定义一个用于创建对象的接口,让子类决定实例化哪一个类。使一个类的实例化延迟到其子类
适用:当一个类不知道它所必须创建的对象的类的时候
类图:
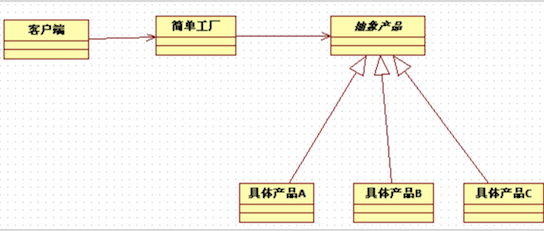
例子代码:
interface IProduct{} class ProductA implements IProduct{} class ProductB implements IProduct{} interface IFactory{ public IProduct getProduct(); } class FactoryA implements IFactory{ public IProduct getProduct(){ return new ProductA(); } } class FactoryB implements IFactory{ public IProduct getProduct(){ return new ProductB(); } } // 工厂方法 class Factory { public IProduct getProductA(){ return new ProductA(); } public IProduct getProductB(){ return new ProductB(); } public IProduct getProduct(int type){ if (type==1){ return new ProductA(); }else{ return new ProductB(); } } } public class TestFactory { public static void test(){ IFactory factory = new FactoryA(); IProduct product =factory.getProduct(); // factory = new FactoryB(); product =factory.getProduct(); } }
二、抽象工厂模式
定义:提供一个创建一系列相关或相互依赖对象的接口,而无需指定它们具体的类
适用:一个系统要独立于它的产品的创建、组合和表示时
与工厂模式的区别:工厂模式的一个工厂接口的子类只能实例化一个产品;抽象工厂能实例多个产品
类图:
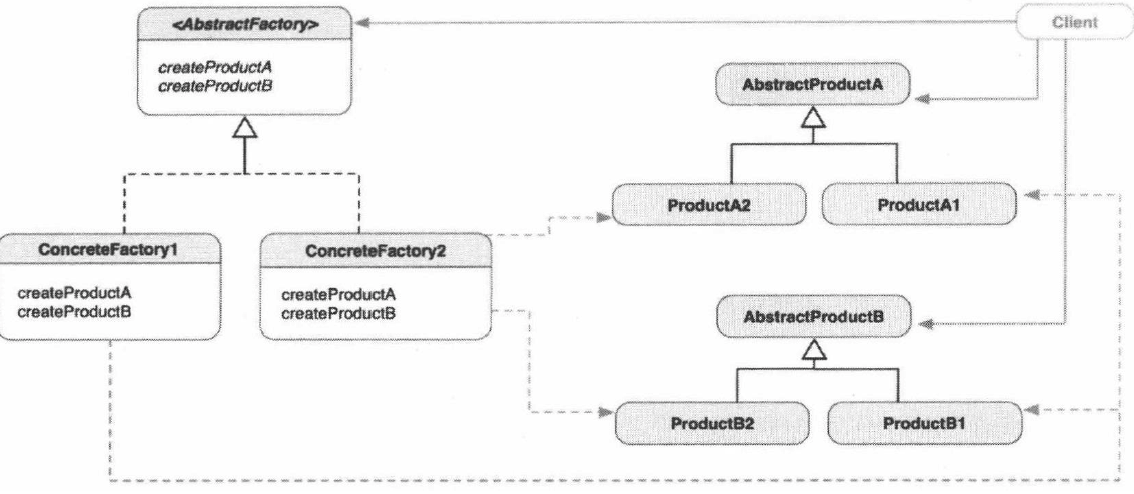
例子代码:
// 产品1 interface IProduct1{} class Product1A implements IProduct1{} // 扩展产品1 B系列 class Product1B implements IProduct1{} // 产品2 interface IProduct2{} class Product2A implements IProduct2{} // 扩展产品2 B系列 class Product2B implements IProduct2{} // 工厂 interface IFactory{ public IProduct1 getProduct1(); public IProduct2 getProduct2(); }; // 工厂 A ,生产A系列产品 class FactoryA implements IFactory{ public IProduct1 getProduct1(){ return new Product1A(); }; public IProduct2 getProduct2(){ return new Product2A(); }; } // 工厂 B ,生产B系列产品 class FactoryB implements IFactory{ public IProduct1 getProduct1(){ return new Product1B(); }; public IProduct2 getProduct2(){ return new Product2B(); }; } public class testAbstractFactory { public void test(){ IFactory factory = new FactoryA(); IProduct1 product1A = (IProduct1)factory.getProduct1(); IProduct2 product2A = (IProduct2)factory.getProduct2(); // 如果扩展产品系列B时,添加 FactoryB、ProductB即可,不需要修改原来代码 factory = new FactoryB(); IProduct1 product1B = (IProduct1)factory.getProduct1(); IProduct2 product2B = (IProduct2)factory.getProduct2(); } }
三、单例模式
具体的请参考:Java设计模式 - 单例模式
单例模式确保某个类只有一个实例,而且自行实现 ,单例模式有以下特点:
1、单例类只能有一个实例。
2、单例类必须自己创建自己的唯一实例。
3、单例类必须给所有其他对象提供这一实例。
定义:保证一个类仅有一个实例,并提供一个访问它的全局访问点。
适用:当类只能有一个实例而且客户可以从一个众所周知的访问点访问它时
四、构造者模式
定义:将一个复杂对象的构建与它的表示分离,使得同样的构建过程可以创建不同的表示
适用:当创建复杂对象的算法应该独立于该对象的组成部分以及它们的装配方式时
也可以参考:Java设计模式-Builder构造者模式
例子代码:
class Person{ private String name; private String address; private int age; private int sex; private int height; private int weight; public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;} public String getName() {return name;} public void setAddress(String address) {this.address = address;} public String getAddress() {return address;} public void setAge(int age) {this.age = age;} public int getAge() {return age;} public void setSex(int sex) {this.sex = sex;} public int getSex() {return sex;} public void setHeight(int height) {this.height = height;} public int getHeight() {return height;} public void setWeight(int weight) {this.weight = weight;} public int getWeight() {return weight;} } class PersonBuilder{ private Person person; public PersonBuilder(){ this.person = new Person(); } public PersonBuilder name(String name){ this.person.setName(name); return this; } public PersonBuilder address(String address){ this.person.setAddress(address); return this; } public PersonBuilder age(int age){ this.person.setAge(age); return this; } public PersonBuilder sex(int sex){ this.person.setSex(sex); return this; } public PersonBuilder height(int height){ this.person.setHeight(height); return this; } public PersonBuilder weight(int weight){ this.person.setWeight(weight); return this; } } public class TestBuilder { public test(){ PersonBuilder builder = new PersonBuilder(); Person person = builder.name("lion") .address("america") .age(18) .sex(2) .height(180) .weight(150); } }
五、原型模式
定义:用原型实例指定创建对象的种类,并且通过拷贝这些原型创建新的对象
适用:当要实例化的类是在运行时刻指定时;或者需要创建多个对象并且这些对象内部状态相差不大
例子代码:
class Car implements Cloneable{ private int id; public int getId() {return id;} public void setId(int id) {this.id = id;} public Car clone(){ try { return (Car)super.clone(); }catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); return null; } } } class Prototype implements Cloneable{ private int id; private Car car; public Car getCar() {return car;} public void setCar(Car car) {this.car = car;} public int getId() {return id;} public void setId(int id) {this.id = id;} public Object clone(){ try { boolean deep = true; if (deep){ /** * 深复制,复制出了两辆车 * */ Prototype prototype = (Prototype)super.clone(); prototype.setCar((Car)this.car.clone()); // 继续复制其他引用对象 return prototype; }else{ /** * 浅复制 ,是同一辆车 * */ return super.clone(); } } catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); return null; } } } public class TestPrototype { public void test(){ Prototype p1 = new Prototype(); p1.setCar(new Car()); p1.setId(1); // 复制 Prototype p2 = (Prototype)p1.clone(); p2.setId(2); } }