前言
本篇来谈一谈图的邻接表实现的两种方式,首先我们明确一点“学会图的邻接表实现的关键点在于“:你所建立的图的邻接表的对象是什么!
首先我们看一下《算法导论》中关于图的邻接表的定义:
图G=(V,E)的邻接表表示有一个包含 |V| 个列表的数组Adj所组成,其中每个列表对应于V中的一个顶点,对于每一个u∈V,邻接表Adj[u]包含所有满足条件(u,v)∈E的顶点v,亦即,Adj[u]包含图G中所有和顶点u相邻的顶点。(或者他也可能指向这些顶点的指针),每个邻接表中的顶点一般以任意的顺序存储。
图的邻接表表示如下图所示:
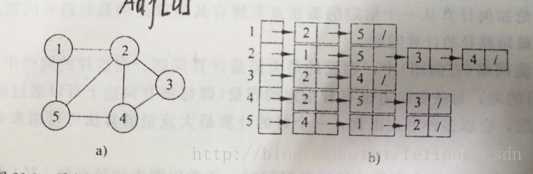
定义总是比较晦涩难懂的,下面我们从如何实现图的邻接表表示来谈一谈!
1、邻接表构建图是必须需要一个Graph对象,也就是图对象!该对象包含属性有:顶点数、边数以及图的顶点集合;
2、正如上面所说,邻接链表的对象首先我们需要确定邻接表的对象,可以用顶点作为邻接链表的对象,自然也可以用边作为邻接链表的对象!下面将分别对这两种方式进行讲解!
一、邻接链表使用顶点作为对象构建图
1、Graph对象类
/**
* 自定义图类
* @author King
*/
public class Graph1 {
Vertex1[] vertexArray=new Vertex1[100];
int verNum=0;
int edgeNum=0;
}
2、Vertex对象类
/**
* 图的顶点类
* @author King
*/
public class Vertex1 {
String verName;
Vertex1 nextNode;
}
3、图的实现类
import java.util.Scanner;
public class CreateGraph3 {
/**
* 根据用户输入的string类型的顶点返回该顶点
* @param graph 图
* @param str 输入数据
* @return返回一个顶点
*/
public Vertex1 getVertex(Graph1 graph,String str){
for(int i=0;i<graph.verNum;i++){
if(graph.vertexArray[i].verName.equals(str)){
return graph.vertexArray[i];
}
}
return null;
}
/**
* 根据用户输入的数据初始化一个图,以邻接表的形式构建!
* @param graph 生成的图
*/
public void initialGraph(Graph1 graph){
@SuppressWarnings("resource")
Scanner scan=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入顶点数和边数:");
graph.verNum=scan.nextInt();
graph.edgeNum=scan.nextInt();
System.out.println("请依次输入定点名称:");
for(int i=0;i<graph.verNum;i++){
Vertex1 vertex=new Vertex1();
String name=scan.next();
vertex.verName=name;
vertex.nextNode=null;
graph.vertexArray[i]=vertex;
}
System.out.println("请依次输入图的便边:");
for(int i=0;i<graph.edgeNum;i++){
String preV=scan.next();
String folV=scan.next();
Vertex1 v1=getVertex(graph,preV);
if(v1==null)
System.out.println("输入边存在图中没有的顶点!");
//下面代码是图构建的核心:链表操作
Vertex1 v2=new Vertex1();
v2.verName=folV;
v2.nextNode=v1.nextNode;
v1.nextNode=v2;
//紧接着下面注释的代码加上便是构建无向图的,不加则是构建有向图的!
// Vertex1 reV2=getVertex(graph,folV);
// if(reV2==null)
// System.out.println("输入边存在图中没有的顶点!");
// Vertex1 reV1=new Vertex1();
// reV1.verName=preV;
// reV1.nextNode=reV2.nextNode;
// reV2.nextNode=reV1;
}
}
/**
* 输入图的邻接表
* @param graph 待输出的图
*/
public void outputGraph(Graph1 graph){
System.out.println("输出图的邻接链表为:");
for(int i=0;i<graph.verNum;i++){
Vertex1 vertex=graph.vertexArray[i];
System.out.print(vertex.verName);
Vertex1 current=vertex.nextNode;
while(current!=null){
System.out.print("-->"+current.verName);
current=current.nextNode;
}
System.out.println();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Graph1 graph=new Graph1();
CreateGraph3 createGraph=new CreateGraph3();
createGraph.initialGraph(graph);
createGraph.outputGraph(graph);
}
}
二、邻接链表使用边作为对象构建图
1、Graph对象类
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class Graph {
ArrayList<Vertex> vertexList=new ArrayList<Vertex>();
int vertexNum=0;
int edgeNum=0;
public Graph(){}
}
2、Edge对象类
/**
* 图的边对象类
* @author King
*/
public class Edge {
int edgeName;
Edge next;
public Edge(){
}
}
3、Vertex对象类<这里顶点对象只是辅助边构建图,不是作为邻接链表的对象>
/**
* 图的点对象类
* @author King
*/
public class Vertex {
String vertexName;
Edge firstEdge=new Edge();
public Vertex(){
}
}
4、图的实现类
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
* 通过构建边和点的对象来创建图
* @author King
*/
public class CreateGraph {
/**
* 根据顶点信息String,返回边的对象
* @param graph 图
* @param str 顶点名称
* @return 返回的是边对象的标签
*/
public int vtoe(Graph graph,String str){
for(int i=0;i<graph.vertexNum;i++){
if(graph.vertexList.get(i).vertexName.equals(str)){
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
/**
* 该函数用于图的初始化的实现
* @param graph 图
*/
public void initialGraph(Graph graph){
@SuppressWarnings("resource")
Scanner scan=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入顶点数和边数:");
graph.vertexNum=scan.nextInt();
graph.edgeNum=scan.nextInt();
System.out.println("请依次输入定点名称:");
for(int i=0;i<graph.vertexNum;i++){
Vertex vertex=new Vertex();
String name=scan.next();
vertex.vertexName=name;
vertex.firstEdge=null;
graph.vertexList.add(vertex);
}
System.out.println("请依次输入每个边:");
for(int i=0;i<graph.edgeNum;i++){
String preV=scan.next();
String folV=scan.next();
int v1=vtoe(graph,preV);
int v2=vtoe(graph,folV);
if(v1==-1 || v2==-1)
System.out.println("输入顶点数据错误!");
//下面代码是图构建的核心:链表操作
Edge edge1=new Edge();
edge1.edgeName=v2;
edge1.next=graph.vertexList.get(v1).firstEdge;
graph.vertexList.get(v1).firstEdge=edge1;
// 下面代码加上便是构建无向图,不加便是构建有向图
// Edge edge2=new Edge();
// edge2.edgeName=v1;
// edge2.next=graph.vertexList.get(v2).firstEdge;
// graph.vertexList.get(v2).firstEdge=edge2;
}
}
/**
* 输出图的邻接链表表示
* @param graph 图
*/
public void outputGraph(Graph graph){
Edge edge=new Edge();
for(int i=0;i<graph.vertexNum;i++){
System.out.print(graph.vertexList.get(i).vertexName);
edge=graph.vertexList.get(i).firstEdge;
while(edge!=null){
System.out.print("-->"+graph.vertexList.get(edge.edgeName).vertexName);
edge=edge.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
CreateGraph createGraph=new CreateGraph();
Graph graph=new Graph();
createGraph.initialGraph(graph);
createGraph.outputGraph(graph);
}
}
5、以上面给出的图片中图为例运行结果展示:

三、使用邻接表构建图的实例
问题:随机生成一个图(可以是有向图或是无向图),图的顶点大概100个左右,若是有向图则边大概2000条左右,若是无向图则边大概1000条左右!并计算出边的入度和出度
代码:
1、Graph类
public class GraphRandom {
VertexRandom[] vertexArray=new VertexRandom[200];
int verNum=0;
int edgeNum=0;
}
2、Vertexl类
public class VertexRandom {
int verName;
int inRadius,outRadius;
VertexRandom nextNode;
}
3、随机图实现类
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
* 随机生成一个图,计算每个顶点的入度和出度
* @author King
*
*/
public class CreateGraph2 {
/**
* 由顶点名称返回顶点集合中的该顶点
* @param graph 图
* @param name 顶点名称
* @return返回顶点对象
*/
public VertexRandom getVertex(GraphRandom graph,int name){
for(int i=0;i<graph.verNum;i++){
if(graph.vertexArray[i].verName==name){
return graph.vertexArray[i];
}
}
return null;
}
/**
* 该顶点通过顶点和边构建图
* @param graph 图
*/
public void randomSpanning(GraphRandom graph){
@SuppressWarnings("resource")
Scanner scan=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入随机图的顶点个数:");
graph.verNum=scan.nextInt();
for(int i=1;i<=graph.verNum;i++){
VertexRandom vertex=new VertexRandom();
vertex.verName=i;
vertex.nextNode=null;
graph.vertexArray[i-1]=vertex;
}
int number=(int)(Math.random()*200+1000);
System.out.println("随机生成的边的数量为:"+number);
graph.edgeNum=number;
for(int i=0;i<graph.edgeNum;i++){
int preV=(int)(Math.random()*100+1);
int folV=(int)(Math.random()*100+1);
while(folV==preV){
folV=(int)(Math.random()*100+1);
}
VertexRandom vertex1=getVertex(graph,preV);
if(vertex1==null)
System.out.println("随机图中没有该顶点!");
VertexRandom vertex2=new VertexRandom();
vertex2.verName=folV;
vertex2.nextNode=vertex1.nextNode;
vertex1.nextNode=vertex2;
// 下面用于计算顶点的出度和入度的
vertex1.outRadius++;
VertexRandom v2=getVertex(graph,folV);
if(v2==null)
System.out.println("随机图中没有该顶点!");
v2.inRadius++;
// 加上下面代码用于产生无向图
// VertexRandom reVertex2=getVertex(graph,folV);
// if(reVertex2==null)
// System.out.println("随机图中没有该顶点!");
// VertexRandom reVertex1=new VertexRandom();
// reVertex1.verName=preV;
// reVertex1.nextNode=reVertex2.nextNode;
// reVertex2.nextNode=reVertex1;
}
}
/**
* 输出图的邻接链表
* @param graph 图
*/
public void outputGraph(GraphRandom graph){
System.out.println("输出图的邻接链表为:");
for(int i=0;i<graph.verNum;i++){
VertexRandom vertex=graph.vertexArray[i];
System.out.print(vertex.verName);
VertexRandom current=vertex.nextNode;
while(current!=null){
System.out.print("-->"+current.verName);
current=current.nextNode;
}
System.out.println();
}
}
/**
* 输出图的入度和出度
* @param graph 图
*/
public void IORadius(GraphRandom graph){
for(int i=0;i<graph.verNum;i++){
System.out.print("顶点"+(i+1)+"的出度为:"+graph.vertexArray[i].outRadius);
System.out.println(",入度为:"+graph.vertexArray[i].inRadius);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
GraphRandom graph=new GraphRandom();
CreateGraph2 createGraph2=new CreateGraph2();
createGraph2.randomSpanning(graph);
createGraph2.outputGraph(graph);
createGraph2.IORadius(graph);
}
}
以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持好代码网。