数学符号都有哪些

2024-11-03 01:08:52
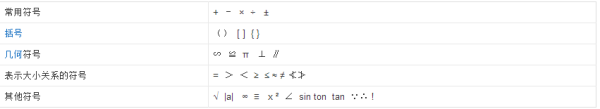
应用数学符号
CRng 交换环范畴
R-mod 环R的左模范畴
Field 域范畴
Poset 偏序集范畴
来历
加号,减号
“+”号是由
也有人说,卖酒的商人用“-”表示
到了十五世纪,德国数学家魏德美正式确定:“+”用作加号,“-”用作减号。
乘号,除号
乘号曾经用过十几种,现在通用两种。一个是“×”,最早是英国数学家奥屈特1631年提出的;一个是“·”,最早是英国数学家赫锐奥特首创的。德国数学家
到了十八世纪,美国数学家欧德莱确定,把“×”作为乘号。他认为“×”是“+”斜起来写,是另一种表示增加的符号。
“÷”最初作为减号,在欧洲大陆长期流行。直到1631年英国数学家奥屈特用“:”表示除或比,另外有人用“-”(除线)表示除。后来瑞士数学家拉哈在他所著的《代数学》里,才根据群众创造,正式将“÷”作为除号。
平方根号曾经用拉丁文“Radix”(根)的首尾两个字母合并起来表示,十七世纪初叶,法国数学家
等于号,不等于号
十六世纪法国数学家维叶特用“=”表示两个量的差别。可是
1591年,法国数学家韦达在菱形中大量使用这个符号,才逐渐为人们接受。十七世纪德国莱布尼茨广泛使用了“=”号,他还在几何学中用“∽”表示相似,用“≌”表示全等。
括号
大括号“{}”和中括号“[]”是代数创始人之一魏治德创造的。

2024-11-03 00:21:21
数学符号的发明及使用比数字要晚,但其数量却超过了数字。现在常用的数学符号已超过了200个,其中,每一个符号都有一段有趣的经历。
1.运算符号:
如加号(+),减号(-),乘号(×或·),除号(÷或/),两个集合的并集(∪),交集(∩),根号(√ ̄),对数(log,lg,ln,lb),比(:),绝对值符号| |,微分(d),积分(∫),闭合曲面(曲线)积分(∮)等。
2.关系符号:
如“=”是等号,“≈”是近似符号(即约等于),“≠”是不等号,“>”是大于符号,“<”是小于符号,“≥”是大于或等于符号(也可写作“≮”,即不小于),“≤”是小于或等于符号(也可写作“≯”,即不大于),“→ ”表示变量变化的趋势,“∽”是相似符号,“≌”是全等号,“∥”是平行符号,“⊥”是垂直符号,“∝”是正比例符号(表示反比例时可以利用倒数关系),“∈”是属于符号,“⊆”是包含于符号,“⊇”是包含符号,“|”表示“能整除”(例如a|b 表示“a能整除b”),x,y等任何字母都可以代表未知数。
3.结合符号:
如小括号“()”,中括号“[ ]”,大括号“{ }”,横线“—”
4.性质符号:
如正号“+”,负号“-”,正负号“
5.省略符号:
∵ 因为
∴ 所以
6.排列组合符号:
C 组合数
A (或P) 排列数
n 元素的总个数
r 参与选择的元素个数
! 阶乘,如5!=5×4×3×2×1=120,规定0!=1
7.离散数学符号
∀ 全称量词
∃存在量词
其他:
在Microsoft Word中可以插入一般应用条件下的所有数学符号,以Word2010软件为例介绍操作方法:第1步,打开Word2010文档窗口,单击需要添加数学符号的公式,并将插入条光标定位到目标位置。第2步,在“公式工具/设计”功能区的“符号”分组中,单击“其他”按钮打开符号面板。默认显示的“基础数学”符号面板。用户可以在“基础数学”符号面板中找到最常用的数学符号。同样地,Alt+41420(即压下Alt不放,依次按41420(小键盘),最后放开Alt 就可以打出 √。

2024-11-03 00:06:32
(2)运算符号:如加号(+),减号(-),乘号(×或·),除号(÷或/),两个集合的并集(∪),交集(∩),根号( ),对数(log,lg,ln),比(∶),微分(d),积分(∫)等。
(3)关系符号:如“=”是等号,“≈”或“ ”是近似符号,“≠”是不等号,“>”是大于符号,“<”是小于符号,“ ”表示变量变化的趋势,“∽”是相似符号,“≌”是全等号,“‖”是平行符号,“⊥”是垂直符号,“∝”是正比例符号,“∈”是属于符号等。
(4)结合符号:如圆括号“()”方括号“[]”,花括号“{}”括线“—”
(5)性质符号:如正号“+”,负号“-”,绝对值符号“‖”
(6)省略符号:如三角形(△),正弦(sin),X的函数(f(x)),极限(lim),因为(∵),所以(∴),总和(∑),连乘(∏),从N个元素中每次取出R个元素所有不同的组合数(C ),幂(aM),阶乘(!)等。
符号 意义
∞ 无穷大
PI 圆周率
|x| 函数的绝对值
∪ 集合并
∩ 集合交
≥ 大于等于
≤ 小于等于
≡ 恒等于或同余
ln(x) 以e为底的对数
lg(x) 以10为底的对数
floor(x) 上取整函数
ceil(x)下取整函数x mod y 求余数
{x} 小数部分 x - floor(x)
∫f(x)δx 不定积分
∫[a:b]f(x)δx a到b的定积分
P为真等于1否则等于0
∑[1≤k≤n]f(k) 对n进行求和,可以拓广至很多情况
如:∑[n is prime][n < 10]f(n)
∑∑[1≤i≤j≤n]n^2
lim f(x) (x->?) 求极限
f(z) f关于z的m阶导函数
C(n:m) 组合数,n中取m
P(n:m) 排列数
m|n m整除n
m⊥n m与n互质
a ∈ A a属于集合A
#A 集合A中的元素个数

2024-11-03 00:13:57
数量符号
X轴Y轴
如:i,
,a,x,e,π。
运算符号
如加号(+),减号(-),乘号(×或·),除号(÷或/),两个集合的并集(∪),交集(∩),根号(√ ̄),对数(log,lg,ln,lb),比(:),绝对值符号| |,微分(d),积分(∫),闭合曲面(曲线)积分(∮)等。
关系符号
如“=”是等号,“≈”是近似符号(即约等于),“≠”是不等号,“>”是大于符号,“<”是小于符号,“≥”是大于或等于符号(也可写作“≮”,即不小于),“≤”是小于或等于符号(也可写作“≯”,即不大于),“→ ”表示变量变化的趋势,“∽”是相似符号,“≌”是全等号,“∥”是平行符号,“⊥”是垂直符号,“∝”是正比例符号(表示反比例时可以利用倒数关系),“∈”是属于符号,“⊆”是包含于符号,“⊇”是包含符号,“|”表示“能整除”(例如a|b 表示“a能整除b”,而
||b表示r是a恰能整除b的最大幂次),x,y等任何字母都可以代表未知数。
结合符号
如小括号“()”,中括号“[ ]”,大括号“{ }”,横线“—”
性质符号
如正号“+”,负号“-”,正负号“
”(以及与之对应使用的负正号“
”)
省略符号
如三角形(△),直角三角形(Rt△),正弦(sin)(见三角函数),
双曲正弦函数(sinh),x的函数(f(x)),极限(lim),角(∠),
总和,连加:∑,求积,连乘:∏,从n个元素中取出r个元素所有不同的组合数
(n元素的总个数;r参与选择的元素个数),幂
等。
排列组合符号
C 组合数
A (或P) 排列数
n 元素的总个数
r 参与选择的元素个数
! 阶乘,如5!=5×4×3×2×1=120,规定0!=1
!! 半阶乘(又称双阶乘),例如7!!=7×5×3×1=105,10!!=10×8×6×4×2=3840
离散数学符号
∀ 全称量词
∃存在量词
├ 断定符(公式在L中可证)
╞ 满足符(公式在E上有效,公式在E上可满足)
﹁ 命题的“非”运算,如命题的否定为﹁p
∧ 命题的“合取”(“与”)运算
∨ 命题的“析取”(“或”,“可兼或”)运算
→ 命题的“条件”运算
↔ 命题的“双条件”运算的
p<=>q 命题p与q的等价关系
p=>q 命题p与q的蕴涵关系(p是q的充分条件,q是p的必要条件)
A* 公式A的对偶公式,或表示A的数论倒数(此时亦可写为
)
wff 合式公式
iff 当且仅当
↑ 命题的“与非” 运算( “与非门” )
↓ 命题的“或非”运算( “或非门” )
□ 模态词“必然”
◇ 模态词“可能”
∅空集
∈ 属于(如"A∈B",即“A属于B”)
∉ 不属于
P(A) 集合A的幂集
|A| 集合A的点数
R²=R○R [R
=R
○R] 关系R的“复合”
ℵ Aleph,阿列夫
⊆ 包含
⊂(或⫋) 真包含
另外,还有相应的⊄,⊈,⊉等
∪ 集合的并运算
U(P)表示P的领域
∩ 集合的交运算
-或\ 集合的差运算
⊕集合的对称差运算
〡 限制
集合关于关系R的等价类
A/R 集合A上关于R的商集
[a] 元素a产生的循环群
I环,理想
Z/(n) 模n的同余类集合
r(R) 关系 R的自反闭包
s(R) 关系 R的对称闭包
CP 命题演绎的定理(CP 规则)
EG 存在推广规则(存在量词引入规则)
ES 存在量词特指规则(存在量词消去规则)
UG 全称推广规则(全称量词引入规则)
US 全称特指规则(全称量词消去规则)
R 关系
r 相容关系
R○S 关系 与关系 的复合
domf 函数 的定义域(前域)
ranf 函数 的值域
f:x→y f是x到y的函数
(x,y) x与y的最大公约数,有时为避免混淆,使用gcd(x,y)
[x,y] x与y的最小公倍数,有时为避免混淆,使用lcm(x,y)
aH(Ha) H关于a的左(右)陪集
Ker(f) 同态映射f的核(或称f同态核)
[1,n] 1到n的整数集合
d(A,B),|AB|,或AB 点A与点B间的距离
d(V) 点V的度数
G=(V,E) 点集为V,边集为E的图G
W(G) 图G的连通分支数
k(G) 图G的点连通度
Δ(G) 图G的最大点度
A(G) 图G的邻接矩阵
P(G) 图G的可达矩阵
M(G) 图G的关联矩阵
C 复数集
I 虚数集
N 自然数集,非负整数集(包含元素"0")
N*(N+) 正自然数集,正整数集(其中*表示从集合中去掉元素“0”,如R*表示非零实数)
P 素数(质数)集
Q 有理数集
R 实数集
Z 整数集
Set 集范畴
Top 拓扑空间范畴
Ab 交换群范畴
Grp 群范畴
Mon 单元半群范畴
Ring 有单位元的(结合)环范畴
Rng 环范畴
CRng 交换环范畴
R-mod 环R的左模范畴
mod-R 环R的右模范畴
Field 域范畴
Poset 偏序集范畴

2024-11-03 00:08:42
01:简介
全球最大的软件公司微软
02:常识
微软,开发软件时,收集的资料应算是全面性的,算是够齐全的了
所以以最微软最普及的办公软件WORD应是够客观的
03:材料
微软 OFFICE WORD 软件
04:操作步验如图示
注意事项:提供的截图接口虽为英文(我会加注中文字),但是请参考相同位置及图标即可
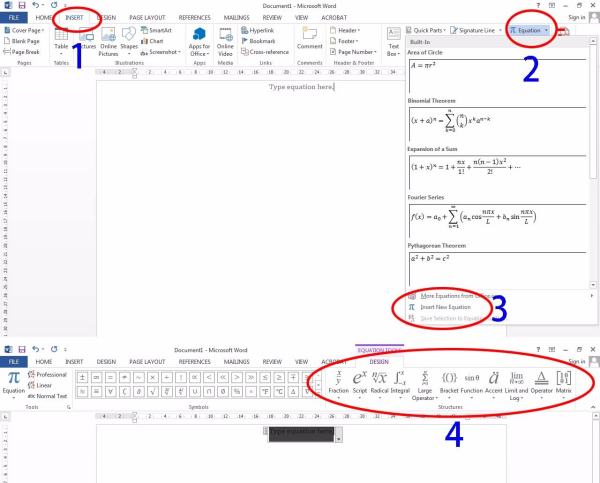
看你须要那个符号
自行复制/粘贴
= equals sign equality 5 = 2+3
5 is equal to 2+3
≠ not equal sign inequality 5 ≠ 4
5 is not equal to 4
≈ approximately equal approximation sin(0.01) ≈ 0.01,
x ≈ y means x is approximately equal to y
> strict inequality greater than 5 > 4
5 is greater than 4
< strict inequality less than 4 < 5
4 is less than 5
≥ inequality greater than or equal to 5 ≥ 4,
x ≥ y means x is greater than or equal to y
≤ inequality less than or equal to 4 ≤ 5,
x ≤ y means x is less than or equal to y
( ) parentheses calculate expression inside first 2 × (3+5) = 16
[ ] brackets calculate expression inside first [(1+2)×(1+5)] = 18
+ plus sign addition 1 + 1 = 2
− minus sign subtraction 2 − 1 = 1
± plus - minus both plus and minus operations 3 ± 5 = 8 and -2
± minus - plus both minus and plus operations 3 ∓ 5 = -2 and 8
* asterisk multiplication 2 * 3 = 6
× times sign multiplication 2 × 3 = 6
⋅ multiplication dot multiplication 2 ⋅ 3 = 6
÷ division sign / obelus division 6 ÷ 2 = 3
/ division slash division 6 / 2 = 3
— horizontal line division / fraction
mod modulo remainder calculation 7 mod 2 = 1
. period decimal point, decimal separator 2.56 = 2+56/100
ab power exponent 23 = 8
a^b caret exponent 2 ^ 3 = 8
√a square root
√a ⋅ √a = a
√9 = ±3
3√a cube root 3√a ⋅ 3√a ⋅ 3√a = a 3√8 = 2
4√a fourth root 4√a ⋅ 4√a ⋅ 4√a ⋅ 4√a = a 4√16 = ±2
n√a n-th root (radical) for n=3, n√8 = 2
% percent 1% = 1/100 10% × 30 = 3
‰ per-mille 1‰ = 1/1000 = 0.1% 10‰ × 30 = 0.3
ppm per-million 1ppm = 1/1000000 10ppm × 30 = 0.0003
ppb per-billion 1ppb = 1/1000000000 10ppb × 30 = 3×10-7
ppt per-trillion 1ppt = 10-12 10ppt × 30 = 3×10-10
∠ angle formed by two rays ∠ABC = 30°
measured angle ABC = 30°
spherical angle AOB = 30°
∟ right angle = 90° α = 90°
° degree 1 turn = 360° α = 60°
deg degree 1 turn = 360deg α = 60deg
′ prime arcminute, 1° = 60′ α = 60°59′
″ double prime arcsecond, 1′ = 60″ α = 60°59′59″
line infinite line
AB line segment line from point A to point B
ray line that start from point A
arc arc from point A to point B = 60°
⊥ perpendicular perpendicular lines (90° angle) AC ⊥ BC
| | parallel parallel lines AB | | CD
≅ congruent to equivalence of geometric shapes and size ∆ABC≅ ∆XYZ
~ similarity same shapes, not same size ∆ABC~ ∆XYZ
Δ triangle triangle shape ΔABC≅ ΔBCD
|x-y| distance distance between points x and y | x-y | = 5
π pi constant π = 3.141592654...
is the ratio between the circumference and diameter of a circle
c = π⋅d = 2⋅π⋅r
rad radians radians angle unit 360° = 2π rad
c radians radians angle unit 360° = 2π c
grad gradians / gons grads angle unit 360° = 400 grad
g gradians / gons grads angle unit 360° = 400 g
Algebra symbols
x x variable unknown value to find when 2x = 4, then x = 2
≡ equivalence identical to
≜ equal by definition equal by definition
:= equal by definition equal by definition
~ approximately equal weak approximation 11 ~ 10
≈ approximately equal approximation sin(0.01) ≈ 0.01
∝ proportional to proportional to
y ∝ x when y = kx, kconstant
∞ lemniscate infinity symbol
≪ much less than much less than 1 ≪ 1000000
≫ much greater than much greater than 1000000 ≫ 1
( ) parentheses calculate expression inside first 2 * (3+5) = 16
[ ] brackets calculate expression inside first [(1+2)*(1+5)] = 18
{ } braces set
⌊x⌋ floor brackets rounds number to lower integer ⌊4.3⌋ = 4
⌈x⌉ ceiling brackets rounds number to upper integer ⌈4.3⌉ = 5
x! exclamation mark factorial 4! = 1*2*3*4 = 24
| x | single vertical bar absolute value | -5 | = 5
f (x) function of x maps values of x to f(x) f (x) = 3x+5
(f ∘ g) function composition (f ∘ g) (x) = f (g(x)) f (x)=3x,g(x)=x-1 ⇒(f ∘ g)(x)=3(x-1)
(a,b) open interval (a,b) = {x | a < x < b} x∈ (2,6)
[a,b] closed interval [a,b] = {x | a ≤ x ≤ b} x ∈ [2,6]
∆ delta change / difference ∆t = t1 - t0
∆ discriminant Δ = b2 - 4ac
∑ sigma summation - sum of all values in range of series ∑ xi= x1+x2+...+xn
∑∑ sigma double summation
∏ capital pi product - product of all values in range of series ∏ xi=x1∙x2∙...∙xn
e e constant / Euler's number e = 2.718281828... e = lim (1+1/x)x , x→∞
γ Euler-Mascheroni constant γ = 0.5772156649...
φ golden ratio golden ratio constant
π pi constant π = 3.141592654...
is the ratio between the circumference and diameter of a circle
c = π⋅d = 2⋅π⋅r
· dot scalar product a · b
× cross vector product a × b
A⊗B tensor product tensor product of A and B A ⊗ B
inner product
[ ] brackets matrix of numbers
( ) parentheses matrix of numbers
| A | determinant determinant of matrix A
det(A) determinant determinant of matrix A
|| x || double vertical bars norm
AT transpose matrix transpose (AT)ij = (A)ji
A† Hermitian matrix matrix conjugate transpose (A†)ij = (A)ji
A* Hermitian matrix matrix conjugate transpose (A*)ij = (A)ji
A -1 inverse matrix A A-1 = I
rank(A) matrix rank rank of matrix A rank(A) = 3
dim(U) dimension dimension of matrix A rank(U) = 3
Probability and statistics symbols
P(A) probability function probability of event A P(A) = 0.5
P(A ∩ B) probability of events intersection probability that of events A and B P(A∩B) = 0.5
P(A ∪ B) probability of events union probability that of events A or B P(A∪B) = 0.5
P(A | B) conditional probability function probability of event A given event B occured P(A | B) = 0.3
f (x) probability density function (pdf) P(a ≤ x ≤ b) = ∫ f (x)dx
F(x) cumulative distribution function (cdf) F(x) = P(X≤ x)
μ population mean mean of population values μ = 10
E(X) expectation value expected value of random variable X E(X) = 10
E(X | Y) conditional expectation expected value of random variable X given Y E(X | Y=2) = 5
var(X) variance variance of random variable X var(X) = 4
σ2 variance variance of population values σ2 = 4
std(X) standard deviation standard deviation of random variable X std(X) = 2
σX standard deviation standard deviation value of random variable X σX = 2
median middle value of random variable x
cov(X,Y) covariance covariance of random variables X and Y cov(X,Y) = 4
A ⊅ B not superset set A is not a superset of set B {9,14,28} ⊅ {9,66}
2A power set all subsets of A
empty set Ø = { } C = {Ø}
complex numbers set = {z | z=a+bi, -∞<a<∞, -∞<b<∞} 6+2i ∈
⋅ and and x ⋅ y
^ caret / circumflex and x ^ y
& ampersand and x & y
+ plus or x + y
∨ reversed caret or x ∨ y
| vertical line or x | y
x' single quote not - negation x'
x bar not - negation x
¬ not not - negation ¬ x
! exclamation mark not - negation ! x
⊕ circled plus / oplus exclusive or - xor x ⊕ y
~ tilde negation ~ x
⇒ implies
⇔ equivalent if and only if (iff)
↔ equivalent if and only if (iff)
∀ for all
∃ there exists
∄ there does not exists
∴ therefore
∵ because / since
∫ integral opposite to derivation ∫ f(x)dx
∫∫ double integral integration of function of 2 variables ∫∫ f(x,y)dxdy
∫∫∫ triple integral integration of function of 3 variables ∫∫∫ f(x,y,z)dxdydz
∮ closed contour / line integral
∯ closed surface integral
∰ closed volume integral
[a,b] closed interval [a,b] = {x | a ≤ x ≤ b}
(a,b) open interval (a,b) = {x | a < x < b}
i imaginary unit i ≡ √-1 z = 3 + 2i
z* complex conjugate z = a+bi → z*=a-bi z* = 3 - 2i
z complex conjugate z = a+bi → z = a-bi z = 3 - 2i
∇ nabla / del gradient / divergence operator ∇f (x,y,z)
Α α Alpha a al-fa
Β β Beta b be-ta
Γ γ Gamma g ga-ma
Δ δ Delta d del-ta
Ε ε Epsilon e ep-si-lon
Ζ ζ Zeta z ze-ta
Η η Eta h eh-ta
Θ θ Theta th te-ta
Ι ι Iota i io-ta
Κ κ Kappa k ka-pa
Λ λ Lambda l lam-da
Μ μ Mu m m-yoo
Ν ν Nu n noo
Ξ ξ Xi x x-ee
Ο ο Omicron o o-mee-c-ron
Π π Pi p pa-yee
Ρ ρ Rho r row
Σ σ Sigma s sig-ma
Τ τ Tau t ta-oo
Υ υ Upsilon u oo-psi-lon
Φ φ Phi ph f-ee
Χ χ Chi ch kh-ee
Ψ ψ Psi ps p-see
Ω ω Omega o o-me-ga
热门标签
