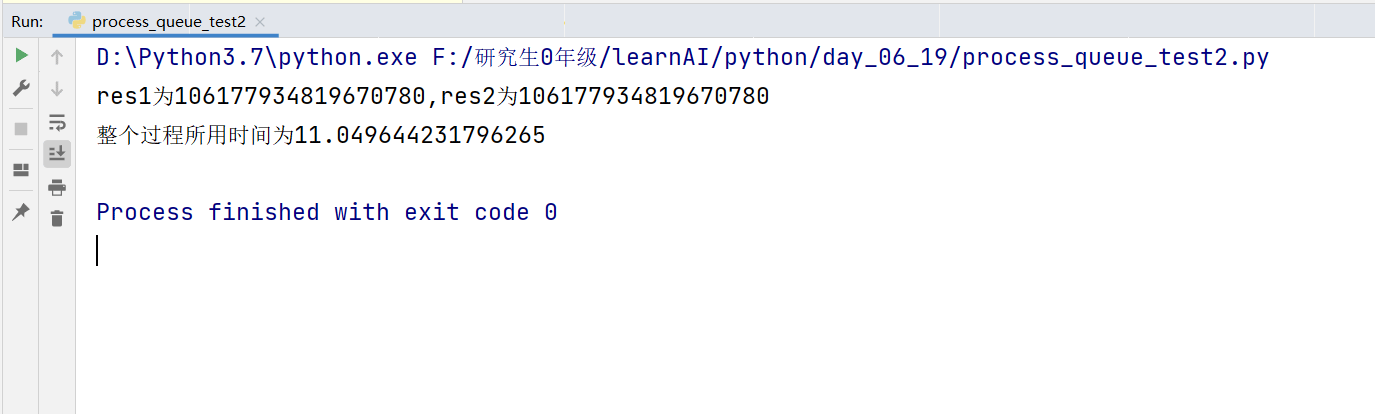
如下所示:
def append(arr, values, axis=None): """ Append values to the end of an array. Parameters ---------- arr : array_like Values are appended to a copy of this array. values : array_like These values are appended to a copy of `arr`. It must be of the correct shape (the same shape as `arr`, excluding `axis`). If `axis` is not specified, `values` can be any shape and will be flattened before use. axis : int, optional The axis along which `values` are appended. If `axis` is not given, both `arr` and `values` are flattened before use. Returns ------- append : ndarray A copy of `arr` with `values` appended to `axis`. Note that `append` does not occur in-place: a new array is allocated and filled. If `axis` is None, `out` is a flattened array.
numpy.append(arr, values, axis=None):
简答来说,就是arr和values会重新组合成一个新的数组,做为返回值。而axis是一个可选的值
当axis无定义时,是横向加成,返回总是为一维数组!
Examples -------- >>> np.append([1, 2, 3], [[4, 5, 6], [7, 8, 9]]) array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9])
当axis有定义的时候,分别为0和1的时候。(注意加载的时候,数组要设置好,行数或者列数要相同。不然会有error:all the input array dimensions except for the concatenation axis must match exactly)
当axis为0时,数组是加在下面(列数要相同):
import numpy as np aa= np.zeros((1,8)) bb=np.ones((3,8)) c = np.append(aa,bb,axis = 0) print(c)
[[ 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0.] [ 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1.] [ 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1.] [ 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1.]]
当axis为1时,数组是加在右边(行数要相同):
import numpy as np aa= np.zeros((3,8)) bb=np.ones((3,1)) c = np.append(aa,bb,axis = 1) print(c)
[[ 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 1.] [ 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 1.] [ 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 1.]]
以上这篇对numpy.append()里的axis的用法详解就是小编分享给大家的全部内容了,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持。