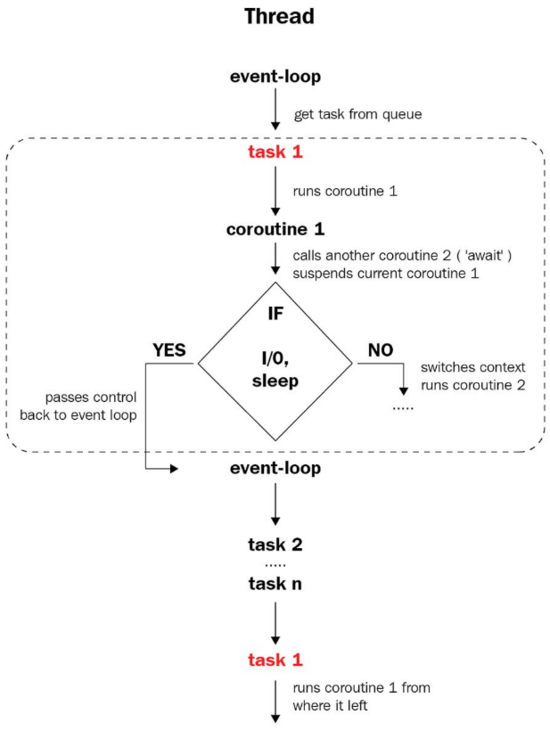
单线程实现多个定时器
NewTimer.py
#!/usr/bin/env pythonfrom heapq import *
from threading import Timer
import threading
import uuid
import time
import datetime
import sys
import mathglobal TimerStamp
global TimerTimesclass CancelFail(Exception):
passclass Slot(object):
def __init__(self, period=0, interval=1, function=None, args=[], kwargs={}):
self.period = period
self.pc = 0
self.interval = interval
self.fire = 0
self.id = uuid.uuid1()
self.function = function
self.args = args
self.kwargs = kwargs#system resolution millisecond
class NewTimer(object): #set enough time make thread sleep, when NewTimer empty set enoug time, too
#make sure sum of your timer call back function execute time shorter than resolution
#todo use a worker thread to operate timer call back function
def __init__(self, resolution=1000):
global TimerStamp
TimerStamp = int(time.time() * 1000) self.nofire = sys.maxint #next fire time interval
self.firestamp = self.nofire + TimerStamp
self.resolution = resolution# 1s self.lock = threading.RLock() self.wait = dict()
self.ready = dict()self._start()
""" private operate ready list """
def _addToReadyList(self, slot, firestamp):
box = dict( [ (slot.id, slot)])
if not self.ready.has_key( firestamp ):
self.ready.update( [(firestamp, box)] )
else:
boxs = self.ready.get(firestamp)
boxs.update( box ) def _delFromReadyList(self, slot):
boxs = self.ready.get(slot.fire)
try:
box = boxs.pop(slot.id)
if not boxs:
self.ready.pop(slot.fire)
except (AttributeError, KeyError):
raise CancelFail """ inside """
def _start(self):
global TimerStamp try:
self.firestamp = sorted( self.ready.keys() )[0]
stamp = float((TimerStamp + self.firestamp - int(time.time()*1000)))/1000
except IndexError:
self.firestamp = self.nofire
stamp = self.nofire try:
self.timer.cancel()
except AttributeError:
pass self.timer = Timer( stamp, self.hander)
self.timer.start() def hander(self, *args, **kwargs):
""" find time arrive slot, do it function """ self.lock.acquire() try:
boxs = self.ready.pop( self.firestamp )
slots = boxs.values()
except KeyError:
slots = [] for slot in slots:
if slot.period:
slot.pc += 1
if slot.pc != slot.period:
slot.fire = slot.interval + slot.fire
self._addToReadyList(slot, slot.fire)
elif slot.period == -1:
slot.fire = slot.interval + slot.fire
self._addToReadyList(slot, slot.fire) """ """
self._start()
self.lock.release()for slot in slots:
try:
slot.function(slot.args, slot.kwargs)
except Exception:
print "slot id %s, timer function fail" % slot.id """ operate new timer manager itself """
def stop(self):
self.timer.cancel() """ new timer manager """
def add(self, period=0, interval=1, function=None, args=[], kwargs={}):
"""
period: one time = 0, times = >0, always = -1
interval: timer fire relative TimerReference
function: when timer fire, call back function
args,kwargs: callback function args
"""
interval = int(interval) * self.resolution#seconds
if interval < self.resolution:
interval = self.resolution slot = Slot( period, interval, function, *args, **kwargs )
box = dict([(slot.id, slot)])
self.wait.update(box) return slot def remove(self, slot):
if isinstance(slot, Slot):
self.cancel(slot) try:
self.wait.pop(slot.id)
except KeyError:
print "wait dict not has the cancel timer" """ timer api """
def reset(self, slot):
if isinstance(slot, Slot):
self.cancel(slot)
slot.pc = 0
self.start(slot) def start(self, slot): def NewTimerStamp(timebase, resolution):
nowoffset = int(time.time() * 1000) - timebase
if nowoffset % resolution < resolution / 10:
currentstamp = nowoffset / resolution
else:
currentstamp = (nowoffset + resolution - 1) / resolution return currentstamp * 1000 global TimerStamp
if isinstance(slot, Slot):
firestamp = slot.interval + NewTimerStamp(TimerStamp, self.resolution)
slot.fire = firestamp self.lock.acquire()
self._addToReadyList(slot, firestamp)
if self.firestamp > slot.fire:
self._start()
self.lock.release() def cancel(self, slot):
if isinstance(slot, Slot):
try:
self.lock.acquire()
self._delFromReadyList(slot)
self._start()
self.lock.release()
except CancelFail:
self.lock.release()def hello( *args, **kargs):
print args[0], datetime.datetime.now()if __name__ == "__main__": print "start test timer", datetime.datetime.now() nt = NewTimer(500)
t0 = nt.add( -1, 5, hello, [0])
t1 = nt.add( 4, 7, hello, [1])
t2 = nt.add( 1, 3, hello, [2])#
t3 = nt.add( 1, 4, hello, [3])#
t4 = nt.add( 4, 5, hello, [4])
t5 = nt.add( 12, 5, hello, [5])#
t6 = nt.add( 9, 7, hello, [6])
t7 = nt.add( 1, 8, hello, [7])#
t8 = nt.add( 40, 1, hello, [8]) nt.start( t0 )
nt.start( t1 )
nt.start( t2 )#
nt.start( t3 )#
nt.start( t4 )
nt.start( t5 )#
nt.start( t6 )
nt.start( t7 )#
nt.start( t8 )nt.cancel(t2)
nt.cancel(t3) nt.remove(t5)
nt.remove(t3) time.sleep(3) nt.start(t2)
nt.cancel(t8) time.sleep(300)
nt.stop() print "finish test timer", datetime.datetime.now()
以上就是python单线程实现多个定时器示例。最可怕的敌人,就是没有坚定的信念。更多关于python单线程实现多个定时器示例请关注haodaima.com其它相关文章!