面向对象程序设计(objective- oriented programming)对于描述复杂的事物,为了从宏观上把握,从整体上合理分析,我们需要使用面向对象
面向对象程序设计(objective- oriented programming)
- 对于描述复杂的事物,为了从宏观上把握,从整体上合理分析,我们需要使用面向对象的思路来分析整个系统。但是,具体到微观操作,仍然需要面向过程的思路去处理
- 面向对象思想是分类的思维模式,思考解决问题需要哪些分类,对这些分类进行单独思考,最后对某个分类下的细节进行面向过程的思索
- 面向过程思想是步骤清晰简单,第一步做什么,第二部做什么
- 面向对象适合处理复杂问题,处理需要多人协作的问题
什么是面向对象
- 面向对象编程的本质:以类的方式组织代码,以对象的组织(封装)数据
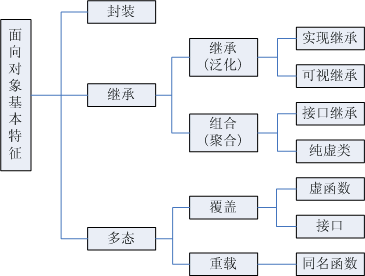
- 面向对象三大特性:封装,继承,多态
- 从认识论角度考虑是先有对象后有类。对象,是具体的事物。类,是抽象的,是对对象的抽象
- 从代码运行的角度考虑是先有类后有对象。类是对象的模板
方法定义与使用
import java.io.IOException;
//Demo01 类
public class Demo01 {
//main 方法
public static void main(String[] args) {
}
/*
修饰符 返回值类型 方法名(...){
//方法体
return 返回值
}
*/
//return 结束方法,返回一个结果,结果可为空
public String sayHello(){
return "hello,world";
}
public int max(int a,int b){
return a>b ? a:b; //三元运算符!
}
//数组下标越界:Arrayindexoutofbounds
public void readFile(String file) throws IOException{
}
}
- 静态方法与动态方法
public class Demo02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//动态方法(无static)需实例化这个类 new+类名
//对象类型 对象名 = 对象值;
//Student student=new Student();
//student.say();
//静态方法(static)可不实例化,直接调用
Student.says();
}
}
==========================================================
//学生类
public class Student {
//非静态方法
public void say(){
System.out.println("学生说话了");
}
//静态方法
public static void says(){
System.out.println("学生说话了");
}
}
==========================================================
public class Demo03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int add=add(1,2);
System.out.println(add);
}
/*
//先用new实例化后再使用
int add = new Demo03().add(1,2);
System.out.println(add);
}
//非静态方法
public int add(int a,int b){
return a+b;
}
*/
//static为静态方法标识符,可在main方法中不实例化直接调用
public static int add(int a,int b){
return a+b;
}
}
值传递与引用传递
public class Demo04 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a=1;
System.out.println(a);
//值传递示例
Demo04.change(a);
System.out.println(a);
}
//返回值为空
public static void change(int a){
a=10;
}
}
==============================================
//引用传递:对象,本质还是值传递
public class Demo05 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person person = new Person();
System.out.println(person.name);//null
Demo05.change(person);
System.out.println(person.name);//秦疆
}
public static void change(Person person){
//person是一个对象,指向的--->Person person=new Person();这是一个具体的人,可以改变属性!
//这里改变的是Person类中name的值;
person.name = "秦疆";
}
}
//定义了一个Person类,有一个属性:name
class Person{
String name; //null
}