相信树形结构大家都知道,但是你是否知道用到了什么设计模式吗?
1、什么是组合模式
Compose objects into tree structures to represent part-whole hierarchies.Composite lets clients treat individual objects and compositions of objects uniformly.
组合模式(Composite Pattern):将对象组合成树形结构以表示“部分-整体”的层次结构, 使得用户对单个对象和组合对象的使用具有一致性。
说人话:用于处理树形结构数据。
2、组合模式定义
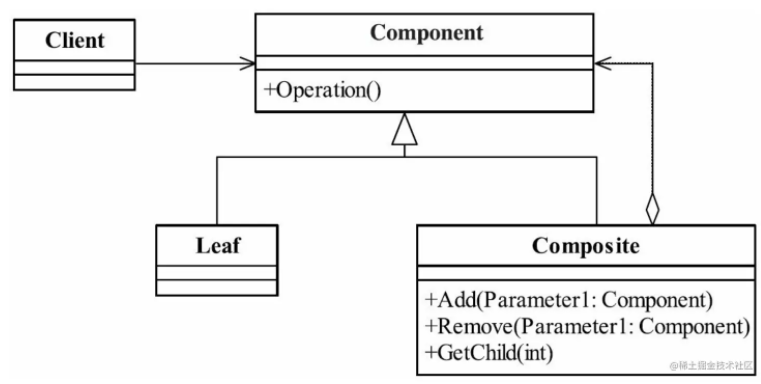
①、Component 抽象构件角色
定义参加组合对象的共有方法和属性,可以定义一些默认的行为或属性。
②、Leaf 叶子节点
叶子对象,其下再也没有其他的子节点,是遍历的最小单位。
③、Composite 树枝构件
树枝对象,作用是组合树枝节点和叶子节点形成一个树形结构。
3、组合模式通用代码实现
/**
* 个体和整体的抽象
*/
public abstract class Component {
// 个体和整体都有的共享
public void doSomething(){
// 通用业务逻辑
System.out.println("通用业务逻辑");
}/**
* 树枝节点
*/
public class Composite extends Component{
// 构件容器
private ArrayList<Component> componentArrayList = new ArrayList<>();
// 增加一个叶子节点或者树枝节点
public void add(Component component){
this.componentArrayList.add(component);
}
// 删除一个叶子节点或者树枝节点
public void remove(Component component){
this.componentArrayList.remove(component);
}
// 获取分支下所有叶子节点和树枝节点
public List<Component> getChildren(){
return this.componentArrayList;
}
}/**
* 叶子节点
*/
public class Leaf extends Component {
// 覆写父类方法
@Override
public void doSomething() {
// 叶子节点逻辑
System.out.println("叶子节点逻辑");
}
}测试:
public class ClientTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建一个根节点
Composite root = new Composite();
root.doSomething();
// 创建一个树枝构件
Composite branch = new Composite();
// 创建一个叶子节点
Leaf leaf = new Leaf();
// 串联起来
root.add(branch);
branch.add(leaf);
display(root);
}
// 通过递归遍历数
public static void display(Composite root){
for(Component c : root.getChildren()){
if(c instanceof Leaf){ // 叶子节点
c.doSomething();
}else{
display((Composite) c);
}
}
}
}这里我们在举一个例子:
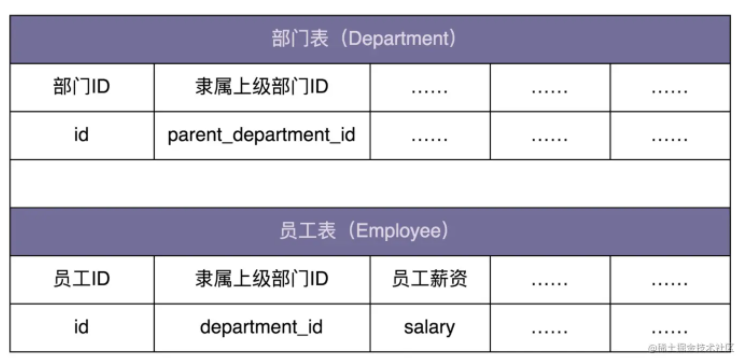
假设我们在开发一个 OA 系统(办公自动化系统)。公司的组织结构包含部门和员工两种数据类型。其中,部门又可以包含子部门和员工。
我们希望在内存中构建整个公司的人员架构图(部门、子部门、员工的隶属关系),并且提供接口计算出部门的薪资成本(隶属于这个部门的所有员工的薪资和)。
/**
* 部门类和员工类的抽象类
*/
public abstract class HumanResource {
protected long id;
protected double salary;
public HumanResource(long id){
this.id = id;
}
public long getId(){
return id;
}
public abstract double calculateSalary();
}public class Department extends HumanResource{
private List<HumanResource> subNodes = new ArrayList<>();
public Department(long id){
super(id);
}
@Override
public double calculateSalary() {
double totalSalary = 0d;
for (HumanResource hr : subNodes){
totalSalary += hr.calculateSalary();
}
this.salary = totalSalary;
return totalSalary;
}
public void addSubNode(HumanResource humanResource){
subNodes.add(humanResource);
}
}public class Employee extends HumanResource{
public Employee(long id,double salary){
super(id);
this.salary = salary;
}
@Override
public double calculateSalary() {
return salary;
}
}测试:
public class PersonClientTest {
private static final long ORGANIZATION_ROOT_ID = 1;
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建总部门
Department root = new Department(ORGANIZATION_ROOT_ID);
// 创建子部门
Department branch = new Department(2L);
// 创建员工
Employee employee1 = new Employee(21L,2000);
Employee employee2 = new Employee(22L,4000);
root.addSubNode(branch);
branch.addSubNode(employee1);
branch.addSubNode(employee2);
double v = root.calculateSalary();
System.out.println(v);
}
private void buildOrganization(Department department){
// 根据 部门id 查询数据库 所有下属部门 id
// List<Long> subDepartmentIds = departmentRepo.getSubDepartmentIds(department.getId());
List<Long> subDepartmentIds = new ArrayList<>();
for (Long subDepartmentId : subDepartmentIds){
Department subDepartment = new Department(subDepartmentId);
department.addSubNode(subDepartment);
buildOrganization(subDepartment);
}
// 根据部门id 查询数据库 其关联员工所有 id
// List<Long> employeeIds = employeeRepo.getDepartmentEmployeeIds(department.getId());
List<Long> employeeIds = new ArrayList<>();
for (Long employeeId : employeeIds){
// 根据 employeeId 查询数据库得到 salary
// 假设为 1000
double salary = 1000d;
department.addSubNode(new Employee(employeeId,salary));
}
}
}4、组合模式优点
①、高层模块调用简单
一棵树形机构中的所有节点都是Component, 局部和整体对调用者来说没有任何区别,也就是说, 高层模块不必关心自己处理的是单个对象还是整个组合结构, 简化了高层模块的代码。
②、节点自由增加
使用了组合模式后, 如果想增加一个树枝节点、 叶子节点都很容易, 只要找到它的父节点就成, 非常容易扩展, 符合开闭原则, 对以后的维护非常有利。
5、组合模式应用场景
只要是树形结构,就可以考虑使用组合模式。
①、维护和展示部分-整体关系的场景, 如树形菜单、 文件和文件夹管理。
②、从一个整体中能够独立出部分模块或功能的场景。
到此这篇关于一文彻底了解Java的组合模式的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关Java组合模式内容请搜索好代码网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持好代码网!