前言
目前,越来越多的管理层(所谓的领导)都希望在手机端查看各种各样的数据报表,以达到随时随地关注经营业绩(监督干活)的目的。这就要求移动端能够提供数据表来满足这类诉求,本篇我们就来介绍 Flutter 的数据表格的使用。通过本篇你会了解到:
- Flutter 自带的
DataTable的使用; - 第三方强大的数据表
SfDataGrid的使用。
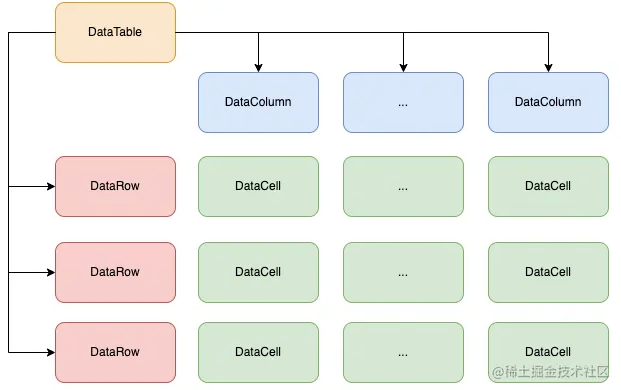
组成DataTable的基本元素
DataTable 是 Flutter 自带的数据表组件,支持定义表头和行数据来实现数据表格,同时支持列排序、选中行等操作,对于基础的数据表格展示基本能够满足,DataTable类的定义如下。
DataTable({
Key? key,
required this.columns,
this.sortColumnIndex,
this.sortAscending = true,
this.onSelectAll,
this.decoration,
this.dataRowColor,
this.dataRowHeight,
this.dataTextStyle,
this.headingRowColor,
this.headingRowHeight,
this.headingTextStyle,
this.horizontalMargin,
this.columnSpacing,
this.showCheckboxColumn = true,
this.showBottomBorder = false,
this.dividerThickness,
required this.rows,
this.checkboxHorizontalMargin,
this.border,
}) 常用的属性说明如下:
columns:是一个DataColumn数组,用于定义表头。rows:是一个DataRow数组,用于定义每一行要显示的数据。sortColumnIndex:要排序的列,可以通过该值设定当前使用那一列进行排序。指定的列会有一个向上或向下的箭头指示当前的排序方式。sortAscending:排序的方式,默认为升序排序。onSelectAll:全选回调事件,如果全选携带的参数为true,否则为false。
DataColumn 是数据列组件,包括了如下4个属性:
label:可以是任意组件,通常我们使用的是Text组件,也可以使用其他组件。tooltip:列的描述文字,用于列宽受限时展示完整的列内容。numeric:是否是数字列,如果是数字列会采用右对齐方式呈现。onSort:排序事件回调,携带两个参数指示当前实用第几列排序,排序方式是升序还是降序。我们可以通过这个方法来响应排序操作对要展示的行数据进行排序。
DataRow是数据行组件,包括如下5个属性:
cells:DataCell数组,用于定义每一列对应的元素。selected:行的选中状态,默认为不选中。onSelectChanged:行选中状态改变时的回调函数。onLongPress:长按行的回调,我们可以用来做长按删除、上移、下移类的操作。color:MaterialStateProperty<Color?>类,可以用来定义不同状态下的行的颜色。
DataCell是数据单元格组件,用于定义要显示的单元格内容以及响应单元格的交互(包括点击、长按、双击等)。 由此我们就得到了一个完整的 DataTable 所需要的元素。
DataTable 示例
首先说一下,Flutter 提供的 DataTable 如果超出屏幕范围默认是不支持滚动的,因此如果要支持滚动,就需要用 SingleChildScrollView 包裹,然后定义滚动的方向来实现横向或纵向滚动。如果要同时支持横向和纵向滚动,就需要使用两个SingleChildScrollView来包裹。下面的示例代码就是实用了两个SingleChildScrollView实现了列表的横向和纵向滚动。
class _DataTableDemoState extends State<DataTableDemo> {
var _sortAscending = true;
int? _sortColumn;
final dataModels = <DataModel>[
DataModel(nation: '中国', population: 14.1, continent: '亚洲'),
DataModel(nation: '美国', population: 2.42, continent: '北美洲'),
DataModel(nation: '俄罗斯', population: 1.43, continent: '欧洲'),
DataModel(nation: '巴西', population: 2.14, continent: '南美洲'),
DataModel(nation: '印度', population: 13.9, continent: '亚洲'),
DataModel(nation: '德国', population: 0.83, continent: '欧洲'),
DataModel(nation: '埃及', population: 1.04, continent: '非洲'),
DataModel(nation: '澳大利亚', population: 0.26, continent: '大洋洲'),
DataModel(nation: '印度', population: 13.9, continent: '亚洲'),
DataModel(nation: '德国', population: 0.83, continent: '欧洲'),
DataModel(nation: '埃及', population: 1.04, continent: '非洲'),
DataModel(nation: '澳大利亚', population: 0.26, continent: '大洋洲'),
];
Function(int, bool)? _sortCallback;
@override
void initState() {
super.initState();
_sortCallback = (int column, bool isAscending) {
setState(() {
_sortColumn = column;
_sortAscending = isAscending;
});
};
}
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
backgroundColor: Colors.white,
appBar: AppBar(
title: const Text('DataTable'),
backgroundColor: Colors.red[400]!,
),
body: SingleChildScrollView(
scrollDirection: Axis.vertical,
child: SingleChildScrollView(
scrollDirection: Axis.horizontal,
child: DataTable(
horizontalMargin: 10.0,
showBottomBorder: true,
sortAscending: _sortAscending,
sortColumnIndex: _sortColumn,
showCheckboxColumn: true,
headingTextStyle: const TextStyle(
fontWeight: FontWeight.bold,
color: Colors.black,
),
columns: [
const DataColumn(label: Text('国家')),
DataColumn(
label: const Text('人口(亿)'),
numeric: true,
onSort: _sortCallback,
),
DataColumn(
label: const Text('大洲'),
onSort: _sortCallback,
),
const DataColumn(label: Text('说明')),
],
rows: sortDataModels(),
),
),
),
);
}
List<DataRow> sortDataModels() {
dataModels.sort((dataModel1, dataModel2) {
bool isAscending = _sortAscending;
var result = 0;
if (_sortColumn == 0) {
result = dataModel1.nation.compareTo(dataModel2.nation);
}
if (_sortColumn == 1) {
result = dataModel1.population.compareTo(dataModel2.population);
}
if (_sortColumn == 2) {
result = dataModel1.continent.compareTo(dataModel2.continent);
}
if (isAscending) {
return result;
}
return -result;
});
return dataModels
.map((dataModel) => DataRow(
onSelectChanged: (selected) {},
cells: [
DataCell(
Text(dataModel.nation),
),
DataCell(
Text('${dataModel.population}'),
),
DataCell(
Text(dataModel.continent),
),
const DataCell(
Text('这是详细介绍'),
),
],
))
.toList();
}
}
上述代码的实现效果如下图所示。
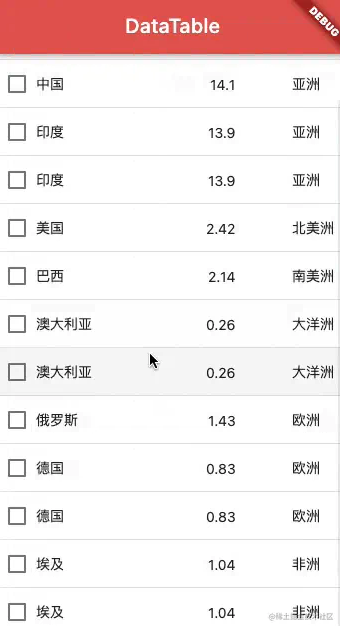
可以看到,使用 DataTable 能够满足我们基本的数据表格的需求,但是我们如果希望表头固定或者列固定,实现起来就有点麻烦了。复杂表格的场景,推荐大家一个好用的第三方库:SfDataGrid。
SfDataGrid
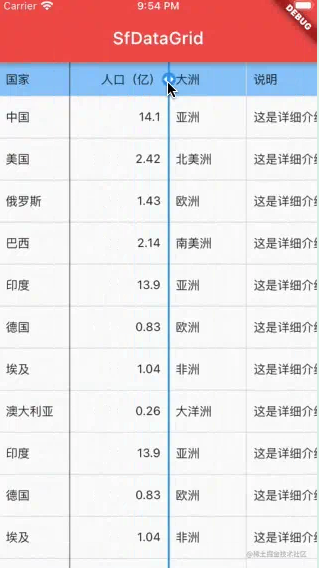
SfDataGrid 同时支持移动端、Web 端和桌面端,基本上和前端 Web 表格功能有的它都有,比如固定某些列或某些行、自动滚动、编辑单元格、设置行高和列宽、排序、单击选择单行或多行、自定义样式、合并单元格、调整列宽、上拉加载或分页浏览、导出到 Excel 文件等等。可以说,用 SfDataGrid 可以满足绝大多数数据表格的场景,更重要的是,官方提供了详细的文档(点此查看使用文档)和示例代码,可以让我们轻松上手。下面是实用 SfDataGrid实现的一个示例效果(移动端列宽调整需要使用长按功能)。
总结
本篇介绍了 Flutter 中的数据表格组件 DataTable 的使用,并介绍了一个很强大的数据表格库 SfDataGrid。如果是简单的数据表格可以使用 Flutter 自带的 DataTable,如果涉及到复杂的样式和交互效果,建议实用 SfDataGrid 来搞定。
到此这篇关于一文带你了解Flutter数据表格的使用的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关Flutter数据表格内容请搜索好代码网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持好代码网!